
Smoking Tobacco
Smoking tobacco can cause serious health problems and can also affect the appearance and health of your mouth and gums.
Side Effects
Tobacco products damage your gum tissue and exposes the tooth roots. Other side effects include:
- Nicotine addiction
- Reduced sense of smell and taste
- Bad breath; stained teeth and recession of the gum line
- Accumulation of tartar (calculus) and plaque
- Increased sensitivity to hot and cold
- Delayed healing after dental work
- Increased heart rate
- Possible breathing difficulties and/or a “smoker’s cough”
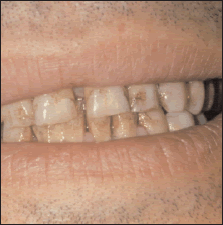
Before: 37-year-old heavy smoker with a heavy build up of dental calculus, stains, and severely offensive tobacco breath.
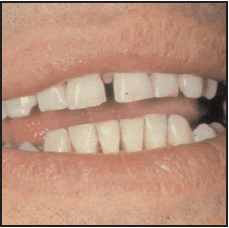
After: After quitting and a thorough cleaning, this smoker’s teeth were restored to their original whiteness. Failure to remain tobacco-free will cause the staining to recur in weeks.
Risk Factors
No matter how long you have smoked, quitting can quickly decrease your risk of developing:
- Oral and pharyngeal (throat) cancers
- Cancers of the lungs and/or other parts of the body
- Heart disease and/or stroke
- Chronic bronchitis, emphysema
- Periodontitis and tooth decay
- Premature aging
- Mouth sores or lesions that do not heal (leukoplakia)
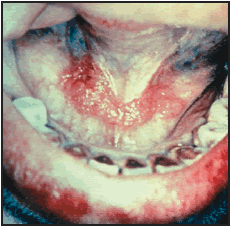
Oral Cancer
How To Quit
- Talk to your dentist and your doctor about developing a strategy to quit.
- Have your dentist screen you for early signs of oral cancer and periodontal disease.
- Anticipate triggers to smoking and prepare strategies on how to avoid them.
- Reward yourself for reaching small goals — go out for dinner or buy yourself a gift.
- Chew sugarless gum and drink water when cravings hit.
- Incorporate exercise into your weekly routine and eat more fruits and vegetables.
Photos provided by Dr. Arden Christen, Indiana University School of Dentistry, Department of Oral Biology.


Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.